- Drivers Control Port Devices List
- Hp Device Drivers
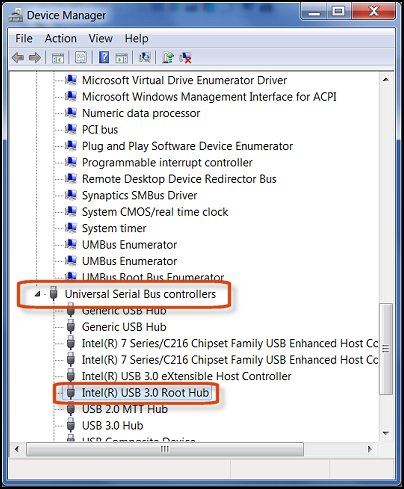
- Usb Port Drivers
- Drivers Control Port Devices Online
 -->
-->Features of the Active USB-COM Port Driver 1.Features: The USB device can be removed from the PC USB Port while the application opens the Serial Port with which the USB; device is connected. (It will be kept opening when the USB device is plugged into the USB Port again.) The Virtual Serial Port is always existed on PC even if USB device is. Some devices will only connect to your computer using a port called 'RS232 Serial Port'. This port was used on old computers before 2003. RS232 was the universal/popular port back in the old days just like USB is today.
To control a peripheral device that is connected to a port on a serial controller, a client application or peripheral device driver sends I/O requests to the port. A client uses IRP_MJ_WRITE and IRP_MJ_READ requests to transmit data to and receive data from a serial port. In addition, Windows defines a set of serial I/O control requests (IOCTLs) that a client can use to configure a serial port.
The serial IRP_MJ_XXX requests and serial IOCTLs together form a serial I/O request interface that is supported across a range of serial controller devices. This interface is supported by the Serial.sys driver, and by the combination of SerCx2 or SerCx and an extension-based serial controller driver.
SerCx2, SerCx, and Serial.sys support many of the same serial IOCTLs. However, SerCx2, SerCx, and Serial.sys support different subsets of the IOCTLs specified in Serial Device Control Requests. The following table summarizes the subsets of IOCTLs that are supported by SerCx2, SerCx, and Serial.sys. A Yes entry in the table indicates that the serial framework extension or driver supports the corresponding IOCTL, and a No entry indicates that it does not.
| Serial IOCTL | SerCx2 | SerCx | Serial.sys |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes | Yes | No | |
No | Yes | Yes | |
See note 1. | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
No | No | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
See note 2. | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
See note 1. | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
IOCTL_SERIAL_GET_MODEM_CONTROL](/windows-hardware/drivers/ddi/ntddser/ni-ntddser-ioctl_serial_get_modem_control)'>IOCTL_SERIAL_GET_MODEM_CONTROL (See note 4.) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
No | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
No | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
No | Yes | Yes | |
No | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
IOCTL_SERIAL_RESET_DEVICE](/windows-hardware/drivers/ddi/ntddser/ni-ntddser-ioctl_serial_reset_device)'>IOCTL_SERIAL_RESET_DEVICE (See note 5.) | No | No | Yes |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
See note 2. | Yes | Yes | |
See note 1. | Yes | Yes | |
See note 1. | Yes | Yes | |
IOCTL_SERIAL_SET_HANDFLOW](/windows-hardware/drivers/ddi/ntddser/ni-ntddser-ioctl_serial_set_handflow)'>IOCTL_SERIAL_SET_HANDFLOW (See note 3.) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
IOCTL_SERIAL_SET_MODEM_CONTROL](/windows-hardware/drivers/ddi/ntddser/ni-ntddser-ioctl_serial_set_modem_control)'>IOCTL_SERIAL_SET_MODEM_CONTROL (See note 4.) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
No | Yes | Yes | |
No | Yes | Yes | |
Yes | Yes | Yes | |
No | Yes | Yes |
Notes

SerCx2 may or may not support this IOCTL depending on the implementation of the serial controller driver and the capabilities of the serial controller hardware.
SerCx2 does not support special characters. SerCx2 always completes an IOCTL_SERIAL_SET_CHARS request with a STATUS_SUCCESS status code, but does not set any special characters or perform any other operation in response to this request. For an IOCTL_SERIAL_GET_CHARS request, SerCx2 sets all the character values in the SERIAL_CHARS structure to null, and completes the request with a STATUS_SUCCESS status code.
SerCx2 and SerCx support only subsets of the flags defined for the FlowReplace and ControlHandShake members of the SERIAL_HANDFLOW structure. Serial.sys supports all of these flags. For more information, see SERIAL_HANDFLOW.
The IOCTL_SERIAL_GET_MODEM_CONTROL and IOCTL_SERIAL_SET_MODEM_CONTROL requests are used primarily for hardware testing. No standard register layout is defined for the modem control operations. Peripheral drivers that use modem control IOCTLs risk making themselves dependent on the hardware features of a particular serial controller.
The Serial.sys driver always completes an IOCTL_SERIAL_RESET_DEVICE request with STATUS_SUCCESS, but performs no operation in response to this request. SerCx2 and SerCx do not support IOCTL_SERIAL_RESET_DEVICE requests and always complete these requests with STATUS_NOT_IMPLEMENTED.
For more information about IOCTL_SERIAL_XXX requests and read and write requests for serial controllers, see the ntddser.h header.
-->The higher-level driver of a class/port pair can sometimes complete IRPs in its DispatchDeviceControl routine. For example a class driver could, during initialization, gather and store information about the features of the underlying device, which might be sought in a subsequent IRP_MJ_DEVICE_CONTROL request, and thus save processing time by satisfying the request without passing it on to the underlying device driver. A class driver might also be designed to check the IRP's parameters and send only requests with valid parameters to the port driver.
Closely coupled class/port drivers also can define a set of driver-specific or device-specific internal I/O control codes that the class driver can use for IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL requests to the port driver.
Drivers Control Port Devices List
For example, the DispatchCreateClose routines in the system keyboard and mouse class drivers send system-defined internal device control requests to enable or disable keyboard and mouse interrupts to the underlying port drivers. These system class drivers set up IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL requests for an underlying port driver. Any new keyboard or mouse port driver that interoperates with these system class drivers also must support these public internal device control requests.
The system parallel class/port driver model has similar features. New parallel class drivers can get support from the system parallel port driver by setting up IRPs for IRP_MJ_INTERNAL_DEVICE_CONTROL requests with public IOCTL_PARALLEL_PORT_XXX control codes. You can replace the system parallel port driver, but any new driver also must support this set of public internal device control requests.
For more information about these public internal device control requests, see device-specific documentation in the Windows Driver Kit (WDK). For information about how to define private I/O control codes, see Using I/O Control Codes.
For a closely coupled pair of port/class drivers, the class driver might handle the processing of certain device control requests without passing them on to the port driver. In a new class/port driver pair, the class driver's DispatchDeviceControl routine can do either of the following:
Hp Device Drivers
Check the validity of the parameters in its own I/O stack location, set the I/O status block if it finds any parameter errors, and call IoCompleteRequest with a PriorityBoost of IO_NO_INCREMENT; otherwise, call IoGetNextIrpStackLocation copy its own I/O stack location into the port driver's, and pass the IRP on with IoCallDriver.
Or, do nothing more than set up the port driver's I/O stack location in the IRP without checking parameters and pass it on to the port driver for processing.
Usb Port Drivers

Drivers Control Port Devices Online
SCSI class drivers have special requirements for handling device control requests. For more information about these requirements, see Storage Drivers.
